This project has three goals for the establishment of the basis of extended central dogma.
- Goal 1: Establishment of glycan information infrastructure
- Goal 2: Establishment of equipment and technology infrastructure
- Goal 3: Establishment of collaboration infrastructure
Goal 1Establishment of glycan information infrastructure
To achieve Goal 1, we have 4 segments in HGA project.
- Comprehensive analysis of human glycan structures (Segment 1: Precise map of human glycoproteome)
- Clarification of relationship between glycans and diseases (Segment 2: Catalog of human disease-related glycome/glycoproteome)
- Clarification of the mechanisms by which glycans are biosynthesized (Segment 3: Glycan biosynthesis atlas)
- Establishment of the infrastructure for using glycan information (Segment 4: The glycan knowledgebase “TOHSA”)
Precise map of human glycoproteome

We will comprehensively clarify the exact structures of glycans present in the human body by using the latest glycan structure analysis technology through mass spectrometry.
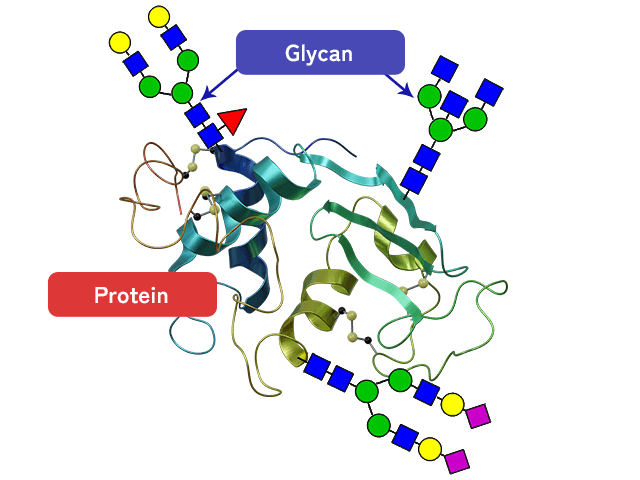
Glycans exist in forms bound to proteins and lipids. The Human Glycan Precise Map will provide detailed information about the specific proteins with corresponding glycan sites and the precise structure of attached glycans.
This map will enable us to comprehend the alterations in glycans that occur during human illnesses and how they differ from the healthy state.
Catalog of human disease-related glycome/glycoproteome
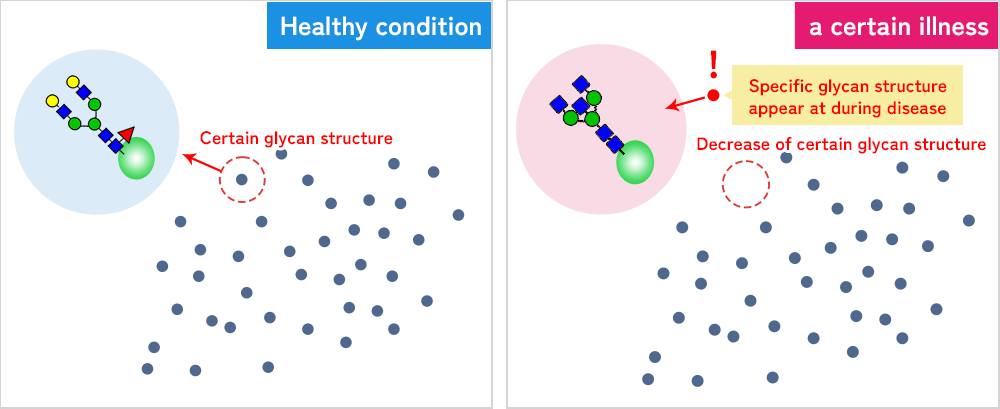
Which glycan changes when and how?
We will investigate the glycans in the blood of various people to elucidate the relationship between physical changes in the body and diseases.

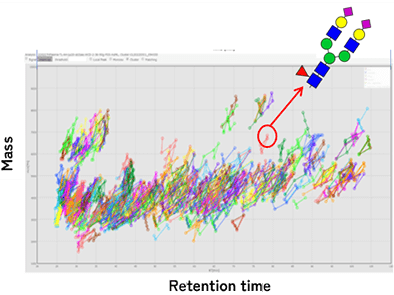
(Glycan analysis image) Each dot shows a different glycan structure.
We will analyze enormous glycan structures in blood. Each dot indicates a distinct glycan structure. It is estimated that a specific glycan is changed when we suffer from disease.
Many current biomarkers for cancer diagnosis detect glycan alterations. This means that disease results in change in a specific glycan. Such glycan alteration sometimes triggers further aggravation of the disease. Based on these knowledge, glycan alterations can be utilized for better diagnosis and therapy.
In this project, based on our “Precise map of human glycoproteome”, we will examine as many structures of glycans as possible using blood samples from patients of dementia and other diseases. Using cutting-edge procedures and equipments, we will analyze enormous glycan structures in blood and clarify what glycans are altered in diseases.
Furthermore, to promptly analyze large amounts of glycans, we also aim to establish the facility enabling automated analysis (Goal 2).
Glycan biosynthesis atlas
How are glycans with various structures produced?
We will elucidate the mechanism by which glycans are synthesized in cells.
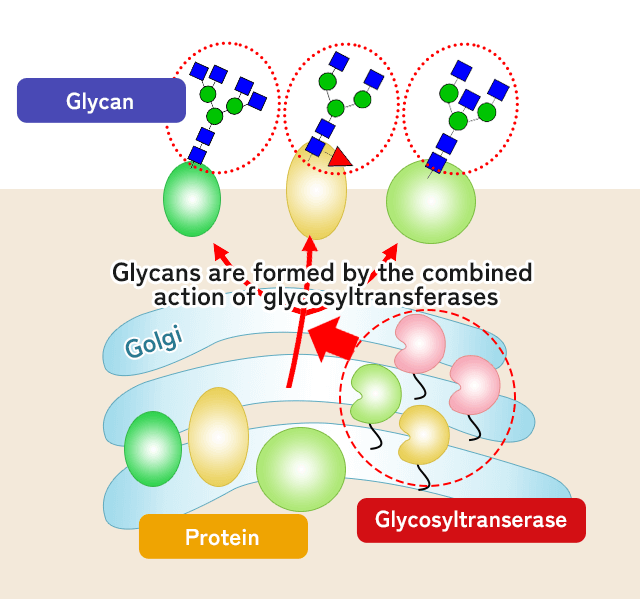
Schematic diagram of how glycans are made in a cell
How does the structural change of glycans occur in disease? If we can understand this, it may be possible to cure diseases by suppressing changes in these glycans.
Glycans are made by the action of enzymes in cells. Many of the enzymes that make glycans (called glycosyltransferases) are present in a place called the Golgi apparatus inside the cell. However, we do not understand much about the details such as the detailed location in the Golgi apparatus and the activity of each enzyme.
In this project, we will clarify the intracellular location and activity details of all human glycosyltransferases. By doing so, we will elucidate the mechanism by which glycans are synthesized, leading to the development of technology to modify specific glycans.
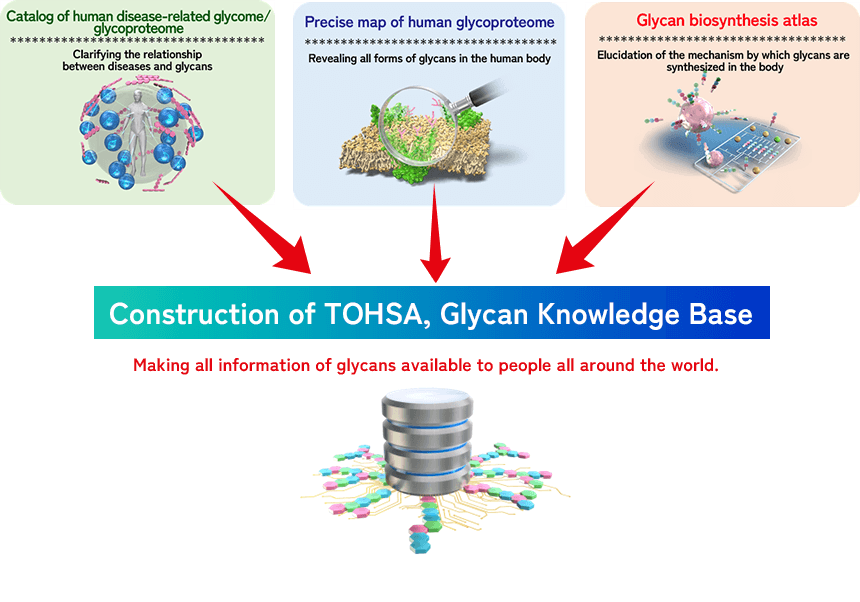
Construction of TOHSA, Glycan Knowledge Base
We will construct a knowledge base called “TOHSA” that comprehensively lists information of human glycans. This will make glycan information available to people all over the world.
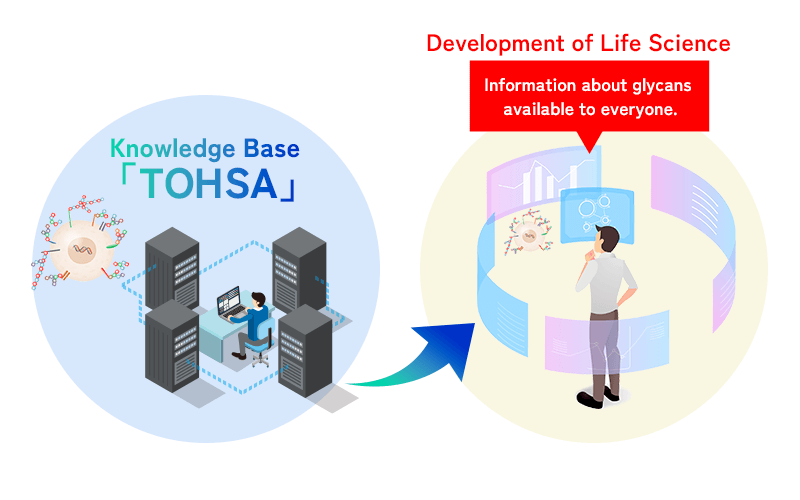
A knowledge base is a system that accumulates and fuses data and knowledge for easy utilization.
“TOHSA” comprehensively lists the structure of glycans in the human body, the relationship between disease and glycans, and the mechanism by which glycans are produced in cells. This valuable information will be made accessible to the public for the benefit of people all over the world.
Information of glycans is widely applied in the research and medical fields, and will be utilized for the true understanding of the mechanism of life and the development of innovative treatment and prevention methods.
Goal 2Establishment of equipment and technology infrastructure
Glycan analysis contains many complicated steps. In this project, to promptly and precisely analyze large amounts of samples, we will develop an innovative facility for automatically conducting the steps.

The first automatic equipment for precisely, safely and quickly conducting complicated glycan extraction steps
The structure of glycans is determined by analyzing data obtained from mass spectrometers. In this project, we will develop software and other tools to accurately determine the location and type of glycans attached to proteins based on mass spectrometry data, thereby establishing the foundation for a global standard method.
A new analytical tool for deciphering complicated glycan structure
Goal 3Establishment of collaboration infrastructure
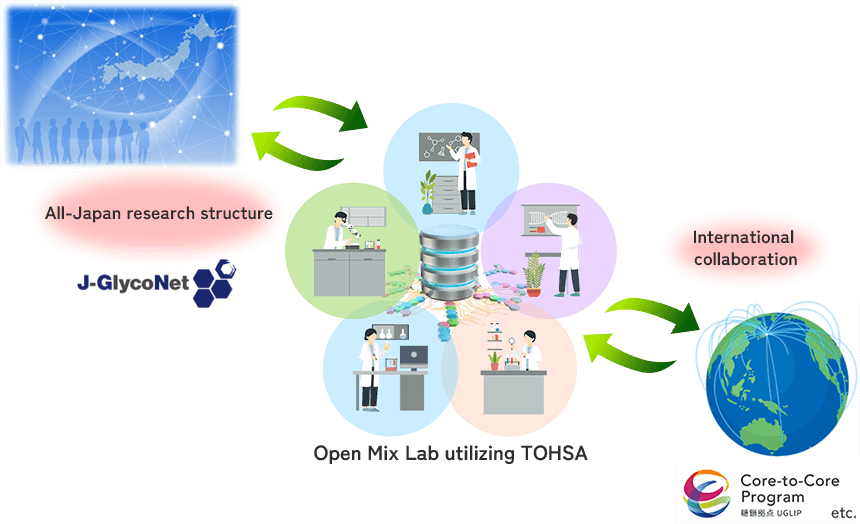
This project is in collaboration with the Joint Usage/Research Center “Glyco Science Cooperative Network (J-GlycoNet)”, which started in FY2022. Glycosciensts from all over Japan are participating in J-GlycoNet as Collaborative Fellows to promote collaborative research on glycans with Japan and foreign countries under an all-Japan structure.
In HGA, using J-GlycoNet platform, we promote usage of knowledgebase TOHSA by domestic and foreign researchers. We also set up Open Mix Lab for joint research using TOHSA and promote international interdisciplinary research.
By such interdisciplinary research, we aim at medical application of glycan structure information and aim to develop glycan-remodeled cells (Neo glycan cells).
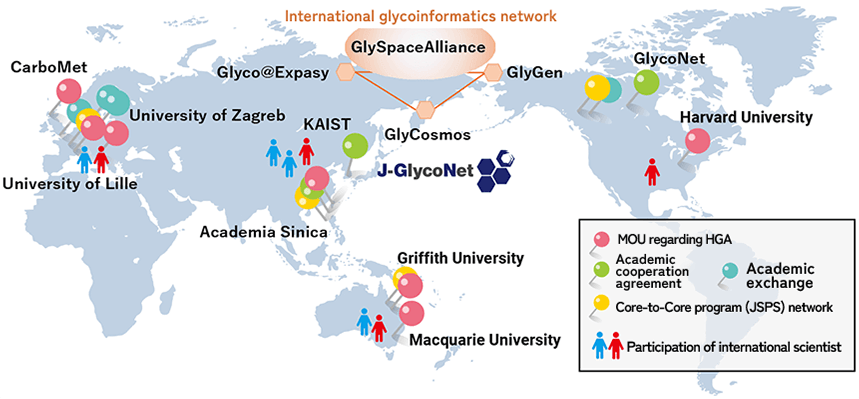
Global network for integrative glycoscience research
Clarification of life principle regulated by glycan
(to extended central dogma)
International collaboration