Human Glycome Atlas Project
This project collects a vast amount of information on human “glycans” and establishes a foundation for the great development of life science and medicine.
Specifically, the project aims to comprehensively obtain information on the structures of “glycans” in the human body, the relationship between diseases and “glycans,” and the mechanism by which “glycans” are produced. We will build such information into a knowledge base* that can be used by people all around the world.
(*Knowledge base: accumulation of data and knowledge)
In addition, this project is supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) under the Large-Scale Academic Frontiers Project(outline of annual plan; only Japanese )

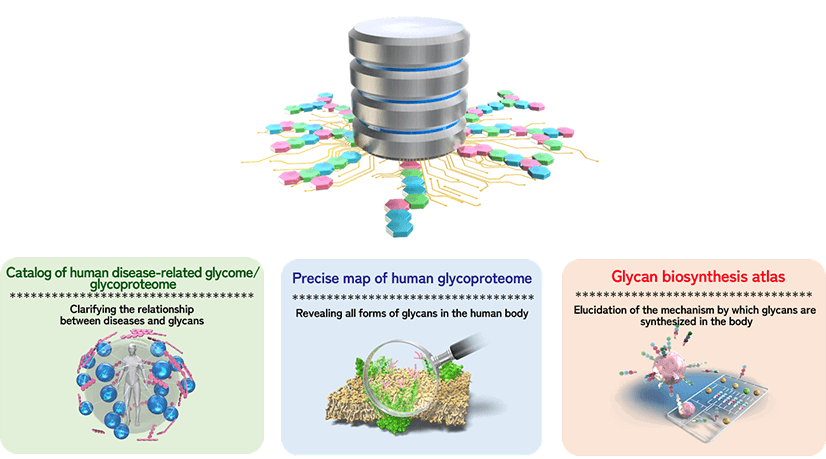
Construction of TOHSA, Glycan Knowledge Base
Making all information of glycans available to people all around the world.
-
Precise map of human glycoproteome
Revealing all forms of glycans in the human body
-
Catalog of human disease-related glycome/glycoproteome
Clarifying the relationship between diseases and glycans
-
Glycan biosynthesis atlas
Elucidation of the mechanism by which glycans are synthesized in the body
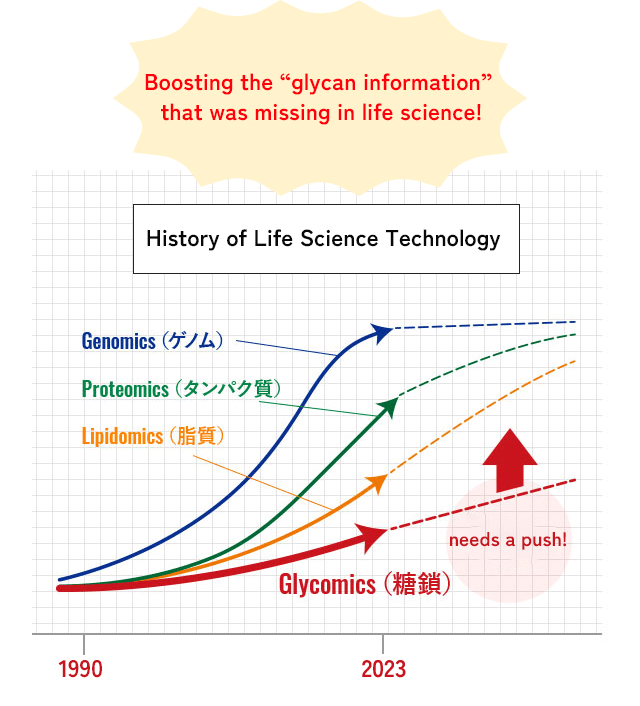
Three life chains (genome, protein, and glycan) are necessary for biological processes. However, regarding the third life chain, “glycan,” our information is far less than the other life chains.
This information about glycan will be widely applied in the fields of research and medicine to deeper understanding of the mechanisms of life and to development of innovative therapeutics and prevention.
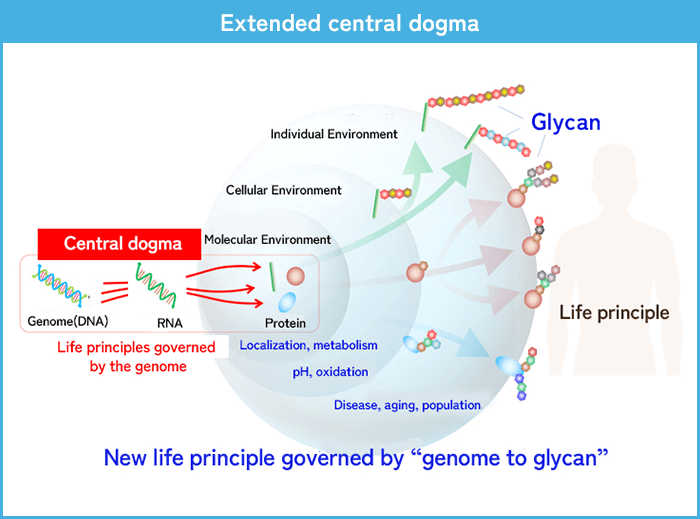
Establishing the basis for a new principle of life
So far, life has been understood based on a principle known as “central dogma”. This is a mechanism whereby RNA is produced from genome (DNA) sequence, and protein is produced from RNA sequence.
However, the surface of all cells is covered with glycans, and many proteins carry glycans. Therefore, it has become clear that biological processes cannot be fully understood only by the central dogma.
The scientific goal of this project is to establish the basis of “extended central dogma,” which adds information on glycans to the existing principle. This will contribute to deeper understanding of life and innovation in medicine.
Three foundations will be developed to discover new life principles from research on glycan
This project has three goals for the establishment of the basis of extended central dogma.
Goal 1 is to comprehensively collect information on glycans and establish a knowledge base “TOHSA” that consolidates such information.
Goal 2 is innovation in equipments and technology. We will develop innovative technologies to collect information on glycans and improve facilities.
Goal 3 is to build an infrastructure for collaboration. We will build and operate a network with domestic and international partners and researchers in other fields and create new knowledge and technologies by utilizing TOHSA.
Goal 1Establishment of glycan information infrastructure
Goal 2Establishment of equipment and technology infrastructure

Goal 3Establishment of collaboration infrastructure